- AUD/JPY positive factors optimistic traction amid the emergence of heavy JPY promoting on Friday.
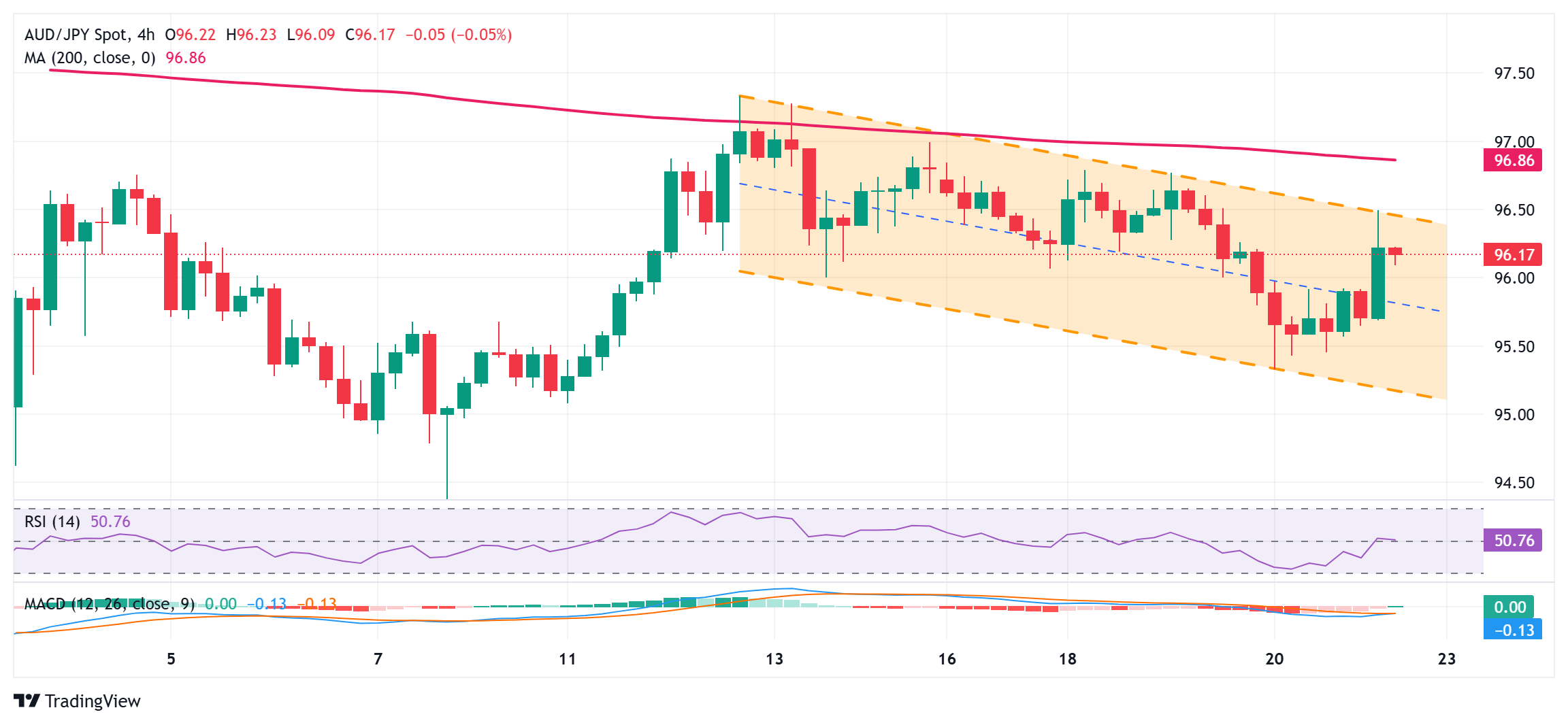
- The intraday momentum stalls close to the highest finish of a one-week-old descending channel.
- A sustained energy past the mentioned barrier ought to pave the way in which for extra positive factors.
The AUD/JPY cross builds on the day prior to this’s late bounce from the 95.35-95.30 space, or over a one-week low, and positive factors sturdy optimistic traction throughout the Asian session on Friday. Spot costs, nevertheless, battle to capitalize on the transfer past mid-96.00 and retreat to the 96.15 area within the final hour, nonetheless up for the primary time in three days.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) weakened after Financial institution of Japan (BoJ) Governor Kazuo Ueda signaled a possible bond market intervention to curb any additional rise within the Japanese authorities bond (JGB) yields. Aside from this, the Reserve Financial institution of Australia’s (RBA) cautious fee minimize earlier this week continues to underpin the Aussie and affords extra help to the AUD/JPY cross. That mentioned, expectations of continued BoJ fee hikes, bolstered by Japan’s sturdy Nationwide CPI, assist restrict the JPY losses and cap the foreign money pair.
From a technical perspective, the sharp intraday move-up stalls close to a resistance marked by the highest finish of over a one-week-old descending pattern channel. The mentioned barrier is pegged close to the 96.45-96.50 space and will now act as a pivotal level. Some follow-through shopping for may carry the AUD/JPY cross to the 200 interval Easy Transferring Common (SMA) on the 4-hour chart, across the 97.00 neighborhood. That is adopted by final week’s swing excessive, across the 97.30-97.35 space, which if cleared ought to pave the way in which for extra positive factors.
The AUD/JPY cross would possibly then resume its latest goodish restoration transfer from the bottom degree since September 2024 touched earlier this month and intention in the direction of reclaiming the 98.00 mark. The momentum may lengthen additional in the direction of the following related hurdle close to the mid-98.00s en path to the 98.75-98.80 provide zone and year-to-date peak, across the 99.10-99.15 area touched in January.
On the flip aspect, the 95.70 space now appears to guard the fast draw back forward of the in a single day swing low, across the 95.35-95.30 area, and the 95.00 psychological mark. A convincing break beneath the latter could be seen as a contemporary set off for bearish merchants and make the AUD/JPY cross weak to retesting the multi-month low, across the 94.40-94.35 area earlier than dropping to the 94.00 round-figure mark.
AUD/JPY 4-hour chart
Financial institution of Japan FAQs
The Financial institution of Japan (BoJ) is the Japanese central financial institution, which units financial coverage within the nation. Its mandate is to situation banknotes and perform foreign money and financial management to make sure value stability, which implies an inflation goal of round 2%.
The Financial institution of Japan embarked in an ultra-loose financial coverage in 2013 with the intention to stimulate the economic system and gasoline inflation amid a low-inflationary atmosphere. The financial institution’s coverage relies on Quantitative and Qualitative Easing (QQE), or printing notes to purchase belongings corresponding to authorities or company bonds to offer liquidity. In 2016, the financial institution doubled down on its technique and additional loosened coverage by first introducing damaging rates of interest after which instantly controlling the yield of its 10-year authorities bonds. In March 2024, the BoJ lifted rates of interest, successfully retreating from the ultra-loose financial coverage stance.
The Financial institution’s huge stimulus brought on the Yen to depreciate towards its fundamental foreign money friends. This course of exacerbated in 2022 and 2023 on account of an rising coverage divergence between the Financial institution of Japan and different fundamental central banks, which opted to extend rates of interest sharply to combat decades-high ranges of inflation. The BoJ’s coverage led to a widening differential with different currencies, dragging down the worth of the Yen. This pattern partly reversed in 2024, when the BoJ determined to desert its ultra-loose coverage stance.
A weaker Yen and the spike in international vitality costs led to a rise in Japanese inflation, which exceeded the BoJ’s 2% goal. The prospect of rising salaries within the nation – a key component fuelling inflation – additionally contributed to the transfer.
