- The US Greenback Index plummeted on Thursday, failing to carry beneficial properties after Wednesday’s inflation-driven rally.
- Stronger-than-expected Producer Worth Index knowledge initially supported the Buck however was offset by geopolitical headlines.
- President Trump and Russian President Putin agreed to start peace talks with Ukraine, decreasing market threat aversion.
- Jobless claims knowledge got here in barely higher than anticipated, reinforcing resilience within the US labor market.
The US Greenback Index (DXY), which measures the worth of the US Greenback in opposition to a basket of currencies, struggles to carry onto beneficial properties following Wednesday’s inflation knowledge. Merchants are fast to dismiss the most recent Producer Worth Index (PPI) figures, shifting their focus to geopolitical developments.
A possible peace settlement between Russia and Ukraine and the most recent US jobless claims knowledge add to the market’s uncertainty, leaving the DXY under 107.30.
Every day digest market movers: US Greenback fails to capitalize on sturdy PPI knowledge
- The PPI for January elevated by 0.4%, exceeding the anticipated 0.3%, however got here down from a revised 0.5% prior.
- Core PPI matched expectations at 0.3%, however December’s determine was revised larger to 0.4%, signaling persistent value stress.
- Preliminary Jobless Claims fell to 213,000 for the week ending February 7, barely under the forecast of 215,000.
- Persevering with Jobless Claims dropped to 1.850 million, under the projected 1.880 million, highlighting labor market resilience.
- A shock geopolitical growth noticed President Trump and President Putin agreeing to start peace negotiations with Ukraine, which sparked a wave of optimism.
- On the Federal Reserve’s aspect, its stance stays cautious with officers set to supply additional steerage on the financial coverage outlook.
- The Federal Sentiment Index stays unchanged however continues to be in hawkish territory, signaling policymakers’ reluctance to ease prematurely.
DXY technical outlook: Index loses grip of 20-day shifting common as bearish stress mounts
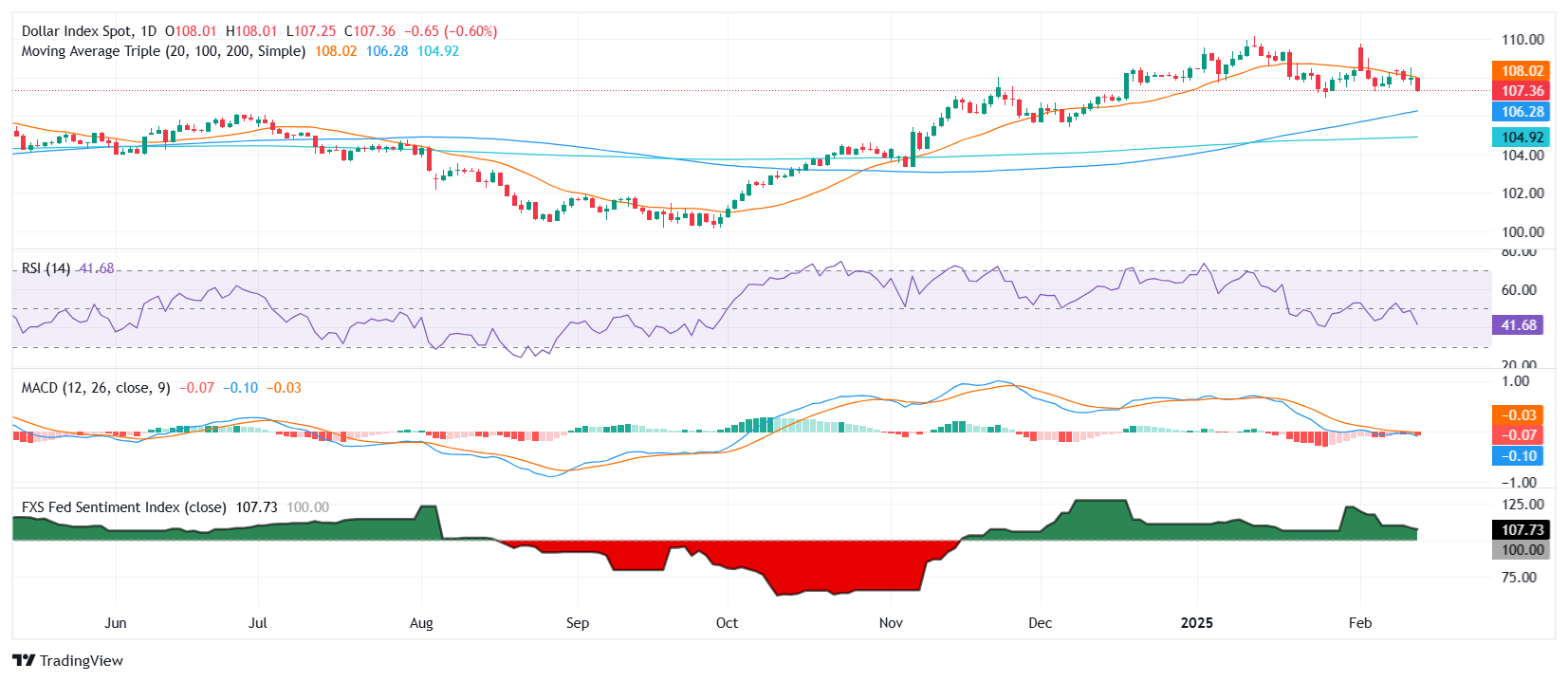
The US Greenback Index struggles to carry above the 20-day Easy Transferring Common (SMA), signaling weak spot after failing to maintain Wednesday’s beneficial properties. The Relative Power Index (RSI) stays under 50, pointing to persistent bearish momentum, whereas the Transferring Common Convergence Divergence (MACD) continues to indicate a destructive pattern.
Fast resistance stands at 108.50 with assist close to 107.80. A break under this degree might speed up declines towards the psychological 107.00 mark.
US Greenback FAQs
The US Greenback (USD) is the official foreign money of the US of America, and the ‘de facto’ foreign money of a major variety of different nations the place it’s present in circulation alongside native notes. It’s the most closely traded foreign money on the earth, accounting for over 88% of all world overseas trade turnover, or a median of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, in keeping with knowledge from 2022. Following the second world warfare, the USD took over from the British Pound because the world’s reserve foreign money. For many of its historical past, the US Greenback was backed by Gold, till the Bretton Woods Settlement in 1971 when the Gold Normal went away.
Crucial single issue impacting on the worth of the US Greenback is financial coverage, which is formed by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to realize value stability (management inflation) and foster full employment. Its main instrument to realize these two targets is by adjusting rates of interest. When costs are rising too shortly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% goal, the Fed will elevate charges, which helps the USD worth. When inflation falls under 2% or the Unemployment Fee is simply too excessive, the Fed could decrease rates of interest, which weighs on the Buck.
In excessive conditions, the Federal Reserve may print extra {Dollars} and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the method by which the Fed considerably will increase the circulate of credit score in a caught monetary system. It’s a non-standard coverage measure used when credit score has dried up as a result of banks won’t lend to one another (out of the concern of counterparty default). It’s a final resort when merely reducing rates of interest is unlikely to realize the required consequence. It was the Fed’s weapon of option to fight the credit score crunch that occurred throughout the Nice Monetary Disaster in 2008. It includes the Fed printing extra {Dollars} and utilizing them to purchase US authorities bonds predominantly from monetary establishments. QE often results in a weaker US Greenback.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse course of whereby the Federal Reserve stops shopping for bonds from monetary establishments and doesn’t reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It’s often optimistic for the US Greenback.
